"Composable Commerce" ist ein modularer Ansatz zum Aufbau von E-Commerce-Plattformen, der es Unternehmen ermöglicht, verschiedene Technologien auszuwählen und zu integrieren, um massgeschneiderte Lösungen zu schaffen. Diese Flexibilität ermöglicht eine schnelle Anpassung an Marktveränderungen und sich wandelnde Kundenbedürfnisse, fördert Innovationen und verschafft einen Wettbewerbsvorteil.
Im schnelllebigen E-Commerce-Sektor sind Flexibilität, Skalierbarkeit und Belastbarkeit wichtiger denn je. Traditionelle monolithische Architekturen, bei denen die gesamte Anwendung als eine einzige, miteinander verbundene Einheit aufgebaut ist, haben sich als unflexibel und schwer zu verwalten erwiesen, insbesondere wenn Unternehmen wachsen und die Anforderungen der Kunden sich ändern.
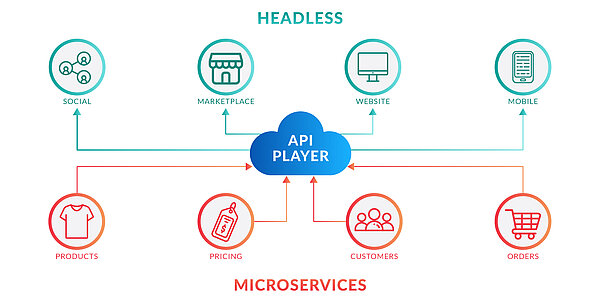
Hier kommt die MACH-Architektur ins Spiel – ein zeitgemässer Ansatz, der die Entwicklung und den Betrieb von E-Commerce-Plattformen revolutioniert. Die MACH-Architektur basiert auf einer Reihe von Technologieprinzipien, die moderne, erstklassige Plattformen unterstützen. Dieses moderne Konzept im E-Commerce steht für Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native und Headless. Jede dieser Komponenten ist entscheidend für den Aufbau einer flexiblen, skalierbaren und effizienten E-Commerce-Plattform.
Microservices
Microservices zerlegen eine grosse Anwendung in kleinere, unabhängige Teile, von denen jedes eine eigene Verantwortung trägt. Jeder Microservice ist ein eigenständiger Dienst, der eine Anwendungsfunktion unterstützt und spezifische Aufgaben übernimmt. Die Microservices kommunizieren über einfache Schnittstellen miteinander, um Geschäftsprobleme zu lösen. Eine E-Commerce-Plattform könnte beispielsweise separate Microservices für Produktkatalog, Benutzerverwaltung, Auftragsabwicklung, Zahlungsabwicklung und Versand haben.
Vorteile:
- Unabhängigkeit: Teams können Microservices unabhängig voneinander entwickeln, bereitstellen und skalieren.
- Flexibilität: Verschiedene Technologien und Programmiersprachen können für die unterschiedlichen Dienste genutzt werden.
- Resilienz: Fehlerisolierung stellt sicher, dass ein Ausfall in einem Dienst nicht das gesamte System beeinträchtigt.
Implementierungsschritte:
- Grenzen identifizieren: Teilen Sie die E-Commerce-Plattform in verschiedene Geschäftsbereiche auf.
- Unabhängig entwickeln: Bilden Sie kleine, spezialisierte Teams, die jeweils für einen Microservice verantwortlich sind.
- Containerisierung nutzen: Verwenden Sie Tools wie Docker und Kubernetes für das effiziente Management und die Bereitstellung von Microservices.
- Kommunikation implementieren: Nutzen Sie leichtgewichtige Protokolle wie HTTP/REST oder Nachrichtenwarteschlangen für die Kommunikation zwischen den Diensten.
API-First
Diese Funktion dient als zentrale Verbindungsstelle in der MACH-Architektur. Sie erleichtert die Synchronisation zwischen verschiedenen Anwendungen oder Microservices und gewährleistet eine nahtlose Integration aller einzelnen Codekomponenten. Durch die Ermöglichung der Interaktion mehrerer Softwareelemente mit anderen Produkten und Dienstleistungen wird der Entwicklungsprozess optimiert. APIs vereinfachen und beschleunigen die Softwareentwicklung und reduzieren so den Zeit- und Ressourcenaufwand.
Vorteile:
- Konsistenz: Gewährleistet einheitliche Kommunikationsstandards über alle Dienste hinweg.
- Interoperabilität: Erleichtert die Integration mit Drittanbieterdiensten und -plattformen.
- Entwicklererfahrung: Vereinfacht die Entwicklung durch klare API-Dokumentation und definierte Schnittstellenverträge.
Implementierungsschritte:
- APIs frühzeitig entwerfen: Definieren Sie APIs vor der funktionalen Implementierung mit Tools wie Swagger/OpenAPI.
- Versionierung beibehalten: Stellen Sie die Abwärtskompatibilität durch effektive API-Versionierung sicher.
- API-Gateways nutzen: Verwalten und sichern Sie APIs mit Lösungen wie Kong oder Apigee.
- Gründlich dokumentieren: Stellen Sie umfassende API-Dokumentation bereit, um Entwicklern zu helfen, sie effektiv zu verstehen und zu nutzen.
Headless
Headless E-Commerce ist derzeit ein führender Trend auf dem Markt. Dabei werden das Frontend und das Backend einer Website entkoppelt, wobei der Datenaustausch über API-Anfragen erfolgt. Diese Konfiguration ermöglicht die unabhängige Entwicklung des Frontends (Head) und erlaubt es, Daten über APIs vom Backend zu beziehen.
Vorteile:
- Omnichannel Erlebnis: Bieten Sie konsistente Benutzererlebnisse über Web, Mobilgeräte, IoT und andere Plattformen hinweg.
- Flexibilität: Wählen Sie unterschiedliche Frontend-Technologien oder -Frameworks, ohne das Backend zu beeinträchtigen.
- Schnellere Iterationen: Entwickeln und implementieren Sie Änderungen am Frontend zügig, ohne das Backend zu beeinflussen.
Implementierungsschritte:
- Frontend und Backend entkoppeln: Stellen Sie sicher, dass Backend-Dienste APIs für die Nutzung durch das Frontend bereitstellen.
- Ein Headless CMS auswählen: Verwenden Sie ein Headless CMS wie Contentful, Strapi oder Sanity zur Inhaltsverwaltung.
- Frontend unabhängig entwickeln: Nutzen Sie moderne Frontend-Frameworks wie React, Vue oder Angular.
- Nahtlose Integration: Sorgen Sie für eine reibungslose Integration zwischen Frontend und Backend durch klar definierte APIs.
Cloud Native
This refers to software where development and delivery are hosted on the cloud. With the business’s constantly changing needs and demands, this model provides out-of-the-box solutions and doesn’t require frequent installation or maintenance. Updates and upgrades happen automatically without any customer effort, downtime, costs, or other fees. Hosting e-commerce on the cloud platform helps in scaling the business infinitely. In this way, cloud infrastructure provides sophisticated scaling capabilities to meet growing demands over time.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay only for the resources you use, optimizing expenses.
- Resilience: Benefit from high availability and disaster recovery options provided by cloud services.
Implementation Steps:
- Choose a Cloud Provider: Select a provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud based on your needs.
- Adopt Cloud Services: Utilize cloud-native services such as managed databases, serverless computing, and auto-scaling groups to enhance flexibility and efficiency.
- Automate Infrastructure: Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation for managing and automating cloud resources.
- Monitor and Optimize: Use monitoring tools to track system performance and optimize the use of resources to ensure efficient operation.
Practical Use Cases of MACH in eCommerce
- Personalization: Utilize microservices for personalized recommendations based on user behaviour data.
- Omnichannel Retail: Implement a headless architecture to provide a seamless shopping experience across online stores, mobile apps, and in-store kiosks.
- Scalable Promotions: Utilize cloud-native services to scale promotional campaigns during peak seasons, ensuring responsiveness under heavy traffic.
- Seamless Integrations: Use APIs to integrate with various third-party services such as payment gateways, shipping providers, and marketing tools.
Challenges and Considerations
- Complexity: Managing multiple microservices and ensuring smooth communication can pose challenges.
- Security: Secure APIs to safeguard functionalities against unauthorized access.
- Data Consistency: Ensure consistent data across microservices through meticulous planning.
- Cost Management: Effectively manage cloud resources to control and optimize costs.
Composable Commerce
MACH Architecture forms the foundation of Composable Commerce. Headlessness, a key aspect of MACH, marks the initial step towards achieving Composable Commerce.
Headlessness dismantles monolithic structures by separating frontend and backend functionalities, enabling them to operate autonomously and enhancing flexibility and agility. However, mere headlessness alone does not fully unlock the spectrum of benefits for modern commerce.
Moving towards composable commerce involves advancing to the next level, where the focus shifts to assembling the customer experience by integrating components like cart, checkout, and order management from diverse vendors. Each component retains independent customization and replacement capabilities, catering precisely to desired customer experiences.

Thus, the principles of Composable Commerce align closely with the MACH architecture.
In a microservices architecture, the entire eCommerce solution is divided into smaller, manageable services that can be individually scaled and managed as needed.
The API-first approach ensures seamless communication between components, even if they are developed by different vendors.
The cloud-native aspect allows businesses to develop and deploy their entire eCommerce solution on any cloud platform, enhancing scalability, security, and reliability.
Closely related to the cloud-native approach is the SaaS model, where applications are hosted online and automatically kept up to date.
A headless approach involves decoupling the frontends from the backends, laying the foundation for a modular architecture that is essential for composability.
Conclusion
In summary, the MACH architecture offers a robust framework for constructing eCommerce platforms in a modular way, adeptly managing the complexities and rapid changes of the digital marketplace. By incorporating microservices, an API-first approach, cloud-native infrastructure, and headless architecture, businesses can achieve:
- Scalability: The capability to expand and efficiently manage increased traffic and workloads.
- Flexibility: The agility to adopt new technologies and meet customer demands swiftly and effectively.
- Resilience: The ability to sustain functionality even when individual components fail.
-
Efficiency: Enhanced operations and streamlined development processes, facilitating faster innovation and deployment.
Adopting the principles of Composable Commerce through MACH architecture enables eCommerce businesses to deliver exceptional customer experiences, respond quickly to market trends, and maintain a competitive edge in the continuously evolving digital landscape.

![[Translate to Deutsch:] Unveiling the Art of Composable Commerce](/fileadmin/_processed_/6/8/csm_MACH-Architecture-large-2_1f49872288.jpg)